Abstract: This software presents diverse utilities to develop the first post-processing layer using the neuromorphic auditory sensor’s (NAS) information. The NAS used implements a cascade filters architecture in FPGA, imitating the behavior of the basilar membrane and inner hair cells, working with the sound information decomposed into its frequency components as spike streams. The neuromorphic hardware interface Address-Event-Representation (AER) is used to propagate auditory information out of the NAS, emulating the auditory vestibular nerve. Using the packetized information (aedat files) generated with jAER software plus an AER to USB computer interface, NAVIS implements a set of graphs that allows to represent the auditory information as cochleograms, histograms, sonograms, etc. It can also split the auditory information into different sets depending on the activity level of the spike streams. The main contribution of this software tool is its capability to apply complex audio post-processing treatments and representations, which is a novelty for spike-based systems in the neuromorphic community. This software will help neuromorphic engineers to build sets for the training of spiking neural networks (SNN).
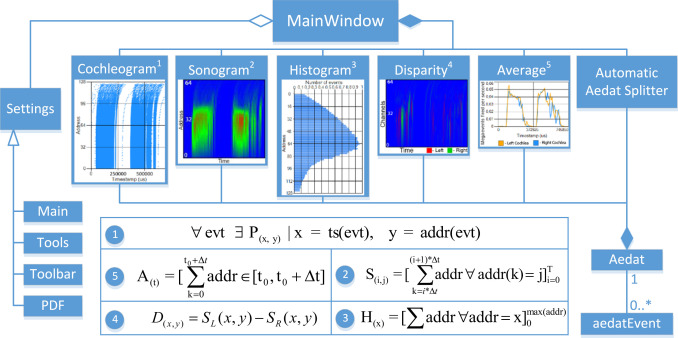
Fig. 1. Block diagram of the overall software architecture describing the algorithms used in the main NAVIS’ functionalities.
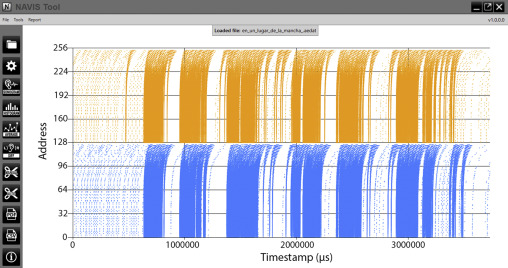
Fig. 2. Cochleogram representing “En un lugar de La Mancha”. Left 64-channels represented in blue and right ones in orange.(For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).
Full text: “NAVIS: Neuromorphic Auditory VISualizer Tool”, Neurocomputing, vol.237 pp. 418-422